Imagine a world where connecting to the internet required running cables through each room. Before Wi-Fi, this was the reality. Today, billions of devices communicate wirelessly, enabling everything from remote work to smart homes. The story of the Wi-Fi patent is filled with accounts of scientific breakthroughs, legal battles over the patent, and a worldwide shift that has shaped our modern methods of connection and interaction.
The Foundations of Wireless Innovation
The history of the Wi-Fi patent traces back to pivotal early wi-fi innovations in radio technology and early experiments in wireless networking. Each advance laid the groundwork for what would become one of the most transformative technologies of the modern era.
The Visionary Minds of Hedy Lamarr and George Antheil
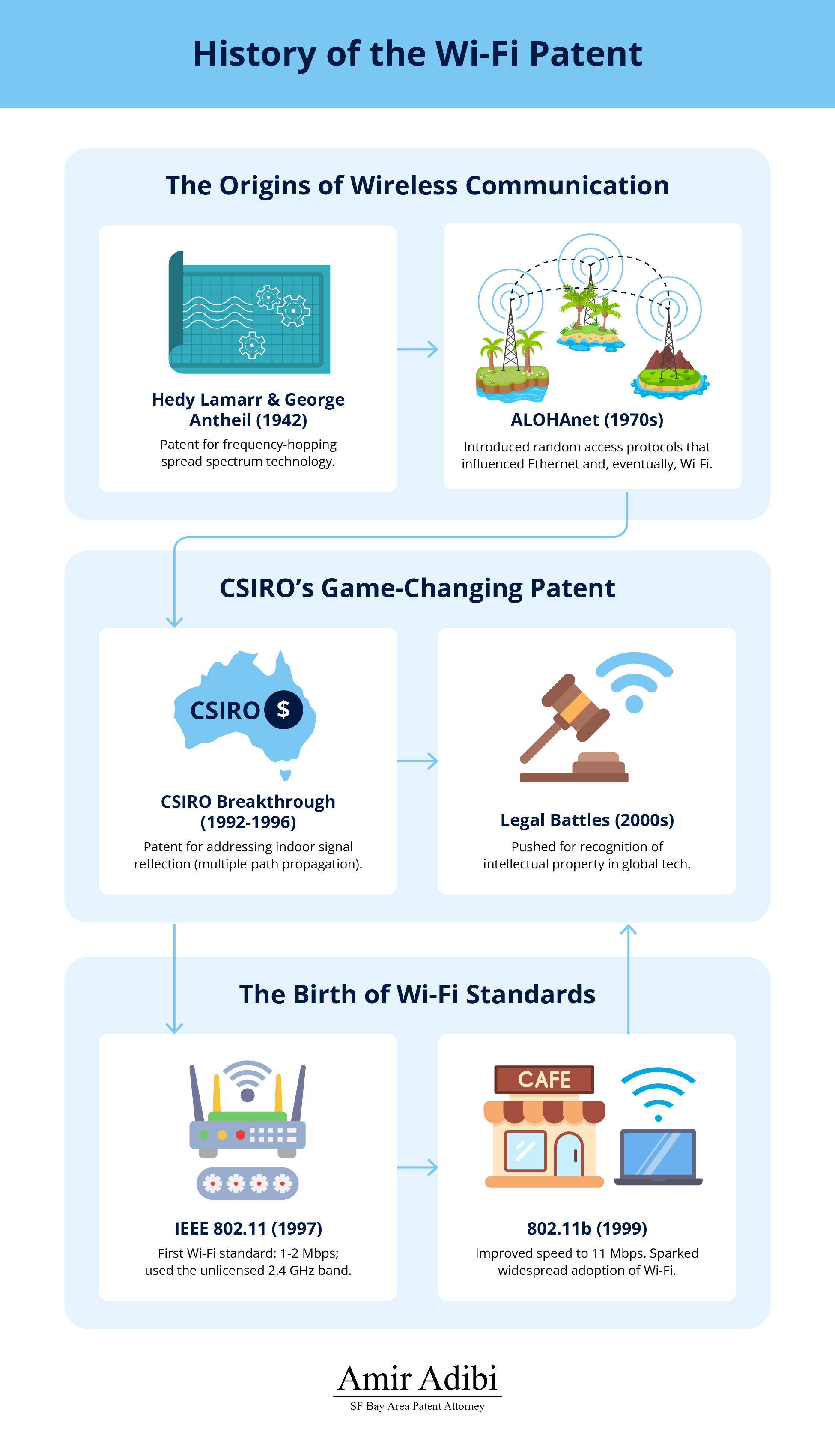
In 1942, Hollywood actress and inventor Hedy Lamarr and avant-garde composer George Antheil filed a patent (US Patent No. 2,292,387) for frequency-hopping spread spectrum technology. Originally designed to guide torpedoes securely by switching radio frequencies to avoid enemy interference, this invention laid the foundation for modern wireless communication.
Though their patent expired long before it was applied commercially, its principles influenced later developments in Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS. Their work highlights how early wi-fi innovations often precede widespread adoption, with their frequency-hopping concept ultimately proving essential to secure, efficient wireless systems. This pivotal invention remains a critical milestone in the history of the Wi-Fi patent, showcasing how unconventional minds contributed to groundbreaking technologies.
ALOHAnet: The Wireless Networking Pioneer
The 1970s brought ALOHAnet, a groundbreaking wireless computer network developed by the University of Hawaii. This system connected island campuses using radio communications, introducing random access protocols that allowed multiple users to share a single communication channel. ALOHAnet’s protocols directly influenced Ethernet and, eventually, Wi-Fi.
By proving the feasibility of packet-based wireless data transmission, ALOHAnet demonstrated how radio waves could be harnessed to create reliable and scalable networks. It was a crucial step in the evolution of wireless connectivity.
The Birth of Wi-Fi Standards
As wireless communication gained traction, the need for universal standards became apparent. These standards provide the framework for the seamless, reliable connections we now take for granted.
IEEE 802.11: The Dawn of Modern Wi-Fi
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) introduced the 802.11 standard in 1997, formally establishing Wi-Fi as a technology. Vic Hayes, often called the “Father of Wi-Fi,” led the working group that developed the standard, initially supporting 1-2 Mbps data rates over the unlicensed 2.4 GHz frequency band.
The release of 802.11b in 1999 marked a turning point. Offering speeds of up to 11 Mbps, it quickly gained widespread adoption. This paved the way for subsequent advancements:
- 802.11g (2003): Increased speeds to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11n (2009): Introduced multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) technology, improving efficiency.
- 802.11ac (2013): Enabled gigabit speeds and multi-user MIMO.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 6E (2020s): Enhanced speed, reduced latency, and expanded bandwidth availability.
These continuous improvements demonstrate the relentless pursuit of faster, more efficient wireless communication, reflecting the dynamic evolution in the history of the Wi-Fi patent and its ongoing influence on modern connectivity.
CSIRO: The Unsung Heroes of Wi-Fi
While IEEE standards provided a framework, a crucial breakthrough from Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) solved fundamental technical challenges in wireless transmission.
CSIRO’s Scientific Breakthrough
During the early 1990s, CSIRO scientists, including John O’Sullivan, tackled the problem of multipath propagation—signal interference caused by reflections in indoor environments. They developed a robust method to enhance wireless data transmission reliability using fast Fourier transform algorithms. In 1992, they filed a patent (granted in 1996) that became foundational to Wi-Fi technology.
The Legal Patent Battles Over Wi-Fi Rights
As Wi-Fi became ubiquitous, CSIRO’s patent became a focal point of contention. The organization engaged in extensive litigation to enforce its intellectual property rights, ultimately securing significant licensing agreements. By 2012, CSIRO had earned over $430 million in royalties, which it reinvested in scientific research. These victories underscored intellectual property’s vital role in fostering innovation while sparking debates about public research and commercialization.
Wi-Fi’s Transformation of Society
Beyond its technical evolution, Wi-Fi has profoundly reshaped society and the global economy. From altering communication patterns to enabling new industries, its impact is pervasive.
Connectivity and Cultural Shifts
Wi-Fi has revolutionized communication, work, and entertainment. The proliferation of wireless hotspots and mobile devices has created an expectation of constant connectivity. This transformation has fueled:
- Remote Work & Telemedicine: Professionals can collaborate globally, while healthcare providers offer virtual consultations.
- Online Education: Learning is no longer confined to classrooms, with digital platforms enabling global access to knowledge.
- Entertainment & Social Media: Streaming services, gaming, and social networks thrive on high-speed wireless access.
Wi-Fi has democratized information, fostering collaboration and creativity across borders.
Economic Impact
The economic implications of Wi-Fi are equally profound. It underpins the digital economy, powering mobile commerce, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Businesses rely on Wi-Fi for operations, from managing inventory to providing customer service.
The Wi-Fi industry itself has grown into a multi-billion-dollar market. Early wi-fi innovations in wireless equipment and services continue to drive economic growth, creating new opportunities for entrepreneurs and tech companies alike.
The Future of Wi-Fi
As Wi-Fi technology evolves, its future applications promise to redefine industries and daily life.
Emerging Technologies & Innovations
Next-generation Wi-Fi, including Wi-Fi 7, aims to enhance efficiency further with ultra-low latency and higher throughput. Potential future applications include:
- Smart Cities: Connected infrastructure optimizing energy use, traffic flow, and emergency response.
- Healthcare: Real-time patient monitoring and remote robotic surgeries enabled by ultra-reliable wireless communication.
- Education: Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) learning environments powered by high-speed Wi-Fi.
Additionally, advancements in Wi-Fi sensing technology could enable devices to detect movement and breathing patterns, opening possibilities for security applications and health monitoring.
Intellectual Property & Legal Considerations
Intellectual property (IP) protection will remain critical as new technologies emerge. Patent strategies will shape the competitive landscape, ensuring innovators can secure and commercialize their breakthroughs. Companies investing in next-generation Wi-Fi should proactively address IP concerns to avoid legal disputes similar to CSIRO’s past patent battles over wi-fi.
Protecting Your Wireless Innovations
From its early theoretical foundations to its transformative impact on society, Wi-Fi has become one of the most vital technologies of the modern era. Its development showcases the power of innovation, legal protection, and ongoing refinement. Understanding the history of Wi-Fi’s patent landscape offers valuable insights into how intellectual property fuels technological progress as the world moves towards even more advanced wireless networks.
Amir Adibi, an experienced patent lawyer, specializes in helping innovators protect their breakthroughs. Expert legal guidance ensures your innovations remain protected in a competitive market, whether you are developing next-generation Wi-Fi technologies, IoT solutions, or wireless communication tools. Amir Adibi can assist in safeguarding your wireless technology innovations and navigating the complex world of intellectual property.



